In today’s world, workforces are distributed, and applications are hosted across multiple environments. Traditional security models, like perimeter-based defenses, struggle to keep pace with the complexity and scale of these modern networks. Enter Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)—a transformative security approach that redefines how organizations protect their data, applications, and users.
In this guide, we’ll explore how ZTNA, within a comprehensive Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) solution such as Timus SASE, enables secure, seamless access to network resources and applications, whether your workforce is remote, on-site, or hybrid.
What is Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)?
ZTNA is a security model that follows the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Unlike traditional VPNs, which provide users with broad network access after the user’s authentication, ZTNA ensures that users are granted access only to the specific applications or services they need based on their identity, device, and context. This minimizes the attack surface and reduces the risk of lateral movement within the network if a user’s credentials are compromised.
In the current realm of a decentralized workplace, where a remote workforce is accessing company resources and cloud-based applications from anywhere, organizations face increasing urgency in securing their networks and protecting sensitive data. In 2022, 1 out of every 5 organizations were the target of security breaches due to remote worker error.
Traditional security measures, such as virtual private networks (VPNs), fall short in providing the granular access control and visibility needed to combat sophisticated cyber threats. These are actively being phased out in favor of more granular access control policies or the Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) security framework.
ZTNA as a Pillar of Zero Trust Architecture
ZTNA is a crucial pillar of Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA), a framework that assumes all network traffic—inside or outside the organization—must be continuously verified before access is granted. At its core, ZTNA asserts that organizations should not automatically trust anyone just because they are inside the network perimeter or that their credentials (username and password) have been checked out. Instead, companies must thoroughly verify the request via rigorous contextual means and policies before granting access to resources.
This approach is especially valuable in today’s cloud-first and remote work environments, where users need secure access to applications from anywhere, using any device.
ZTNA moves beyond the physical limitations set by the four walls of an office and hardware appliances such as on-premise firewalls. It leverages a Software Defined Perimeter based on Zero Trust principles. Key features include:
- Least Privilege Enforcement: Users are granted access only to the resources they are authorized to use. This minimizes the threat surface and reduces the blast radius in case of a breach. Users cannot move laterally within the network.
- Role-Based Access Policies: Admins enforce company security policies based on user-defined roles and permissions.
- Verification for Third Parties: Third parties such as IT contractors or partners must be properly verified before logging into any company resource, typically through a layered Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) process.
By focusing on identity verification, granular access controls, and contextual security checks, ZTNA enhances an organization’s ability to protect sensitive data and resources while ensuring seamless and secure remote access.
How Does ZTNA Work?
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) operates based on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Unlike traditional security approaches, ZTNA does not automatically trust users or devices based on location, such as inside a corporate network. Instead, ZTNA continuously authenticates and authorizes users, ensuring that every request for access to an application or resource is verified.
ZTNA enforces strict access control, providing users with secure, least-privileged access to specific applications or services based on their identity, device status, and other contextual factors like location and behavior. This model contrasts with traditional VPNs and network security solutions, which provide broad network access after a user is authenticated.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of how ZTNA works:
1. User Authentication
The first step in ZTNA is verifying the identity of the user who is requesting access. This is done using identity-based access controls. ZTNA integrates with identity providers, often using Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to ensure the user is who they claim to be. Authentication methods can include:
- Username and password (though in many cases, password-less methods are becoming more common).
- Biometric authentication, such as fingerprints or facial recognition.
- One-time passcodes sent to mobile devices or hardware tokens.
2. Device Health Check
After authenticating the user, ZTNA evaluates the device the user is using. This is crucial because a compromised or non-compliant device can pose a significant security risk, even if the user’s identity has been verified. ZTNA performs a device health check to ensure the device meets the organization’s security policies. This evaluation may include checking the following:
- Whether the device has up-to-date antivirus software installed and running.
- If the operating system is updated with the latest security patches.
- Whether the device is encrypted.
- If the device is connected through a secure network (e.g., it’s not on a public Wi-Fi network without protection).
For example, a remote worker attempts to access a financial application using a personal laptop. ZTNA checks the laptop’s status and finds that the device’s antivirus software is outdated. In this case, access may be denied or restricted until the device is compliant, ensuring that security vulnerabilities are minimized.
This device-centric security step ensures that only healthy, trusted devices can access sensitive corporate resources, reducing the risk of malware-infected or poorly configured devices.
3. Contextual Access Policies
ZTNA goes beyond just identity and device checks by incorporating contextual information to fine-tune access control decisions. This contextual information can include:
- Geographical location: Is the user accessing the network from a known or unknown location? Are they in a trusted region, or is the request coming from a high-risk country where the organization typically does not operate?
- Time of access: Is the access request happening during business hours, or is it an unusual time of day for the user?
- Network environment: Is the user on a secure, corporate network, or are they accessing the application from a public Wi-Fi connection?
- Historical behavior: Does this access request match the user’s normal behavior? For example, if a user typically accesses the system from one country and suddenly requests access from a different, far-off location, ZTNA might trigger additional authentication steps.
Based on these contextual factors, ZTNA dynamically adjusts access. If something appears suspicious—such as a user attempting to access sensitive data from an unfamiliar or high-risk location—the system may require additional authentication (e.g., re-entering a code sent to their mobile device) or deny access altogether.
4. Granular, Least-Privileged Access
One of the core benefits of ZTNA is that it enforces least-privileged access. This means that users are only given access to the specific applications or resources they need to perform their tasks—no more, no less. ZTNA limits the user’s access to individual applications rather than providing access to the entire corporate network, which is common in VPNs.
ZTNA solutions use micro-segmentation to divide the network into smaller, isolated segments. Each segment can have its own access controls, meaning users can only interact with the segments they’re authorized to use. This minimizes the risk of lateral movement, which occurs when attackers gain unauthorized access to other parts of the network after compromising a user’s credentials.
For example, a marketing manager needs access to the company’s digital asset management system to update promotional materials. ZTNA allows users access only to that specific application rather than the entire network. They won’t be able to access sensitive financial data or the development team’s software repositories, limiting potential damage in case their credentials are compromised.
5. Session-Specific Access
ZTNA operates on a session-specific basis, meaning each access request is authenticated, authorized, and encrypted for a single session only. Once the session ends, the user must be re-authenticated for subsequent access. This means that even if an attacker hijacks a session or gains access during a single session, they won’t be able to maintain access for extended periods without passing the authentication checks again.
Session-specific access also provides additional layers of security, as ZTNA can continuously monitor the user’s behavior during the session. If abnormal behavior is detected, such as attempting to access unauthorized applications or making multiple suspicious requests, ZTNA can terminate the session or require further verification.
6. Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Unlike traditional network security models that rely on a single authentication event at the time of login, ZTNA continuously monitors the user’s activity during their session. This ongoing evaluation helps detect suspicious or malicious behavior that might indicate a compromise.
If a user’s behavior changes or the security posture of their device degrades during a session (e.g., their device becomes infected with malware), ZTNA can adjust the user’s access dynamically, restricting or revoking access based on the newly detected threat.
As an example, during a remote work session, an employee’s device suddenly starts communicating with a known malware server. ZTNA detects this unusual behavior and immediately terminates the session, blocking further access to company applications and preventing the potential spread of malware within the network.
By implementing continuous monitoring and dynamically adjusting access, ZTNA ensures that threats are detected and mitigated in real-time rather than relying on periodic security reviews.
ZTNA vs VPN
While VPNs have been widely used to provide remote access, they have limitations in terms of security, scalability, flexibility, and granular control. ZTNA overcomes these limitations by focusing on identity-based authentication, granular access control, and application segmentation. Unlike VPNs, ZTNA solutions default to deny, only granting access to specific applications or resources based on user authentication and authorization. This approach significantly reduces the attack surface and provides organizations with better control and visibility over remote access.
Implementing a Zero Trust Security Framework
Implementing a Zero Trust Security Framework requires careful planning and consideration of an organization’s specific needs and requirements. While each implementation may vary, there are some key steps that organizations can follow to successfully deploy ZTNA and enhance their security posture.
Step 1: Assess Assets and Vulnerabilities
The first step in implementing a Zero Trust Security Framework is to assess the value and vulnerability of an organization’s assets. This involves identifying critical applications, data, and resources, as well as potential security risks and vulnerabilities. By understanding the organization’s assets and vulnerabilities, organizations can develop effective access control policies and security measures.
Step 2: Define Access Control Policies
Once assets and vulnerabilities have been identified, organizations can define access control policies based on the principle of least privilege. Access control policies should be granular, ensuring that users have only the necessary access to perform their tasks. This includes defining user roles, permissions, and authentication methods, as well as making sure a layered MFA is implemented for additional security.
Step 3: Establish Continuous Monitoring and Verification
Continuous monitoring and verification are essential components of a Zero Trust Security Framework. Organizations should implement mechanisms to continuously monitor user behavior, device posture, and application activity to detect any anomalies or suspicious activities. This allows organizations to promptly respond to potential threats and take appropriate actions to mitigate risks.
Step 4: Educate and Train Employees
Implementing a Zero Trust Security Framework requires the collaboration and cooperation of all employees. Organizations should invest in employee education and training programs to raise awareness about the importance of security and the role each individual plays in maintaining a secure environment. This includes educating employees about best practices for password management, recognizing phishing attempts, and reporting any suspicious activities.
Step 5: Regularly Update and Improve Security Measures
Security is an ongoing process, and organizations should regularly update and improve their security measures to stay ahead of emerging threats. This includes keeping software and systems up to date with the latest patches and security updates, conducting regular security audits and assessments, and staying informed about new security trends and technologies.
By following these steps and implementing a Zero Trust Security Framework, organizations can enhance their security posture and protect their sensitive data from evolving cyber threats.
Zero Trust Network Security and Timus
Timus is a cloud-based zero-trust network security platform developed to protect an organization’s local & cloud resources with zero trust policies.
Timus helps companies orchestrate secure access regardless of location and device while protecting the network against cyberattacks. It also provides deep visibility into network activities and helps with compliance.
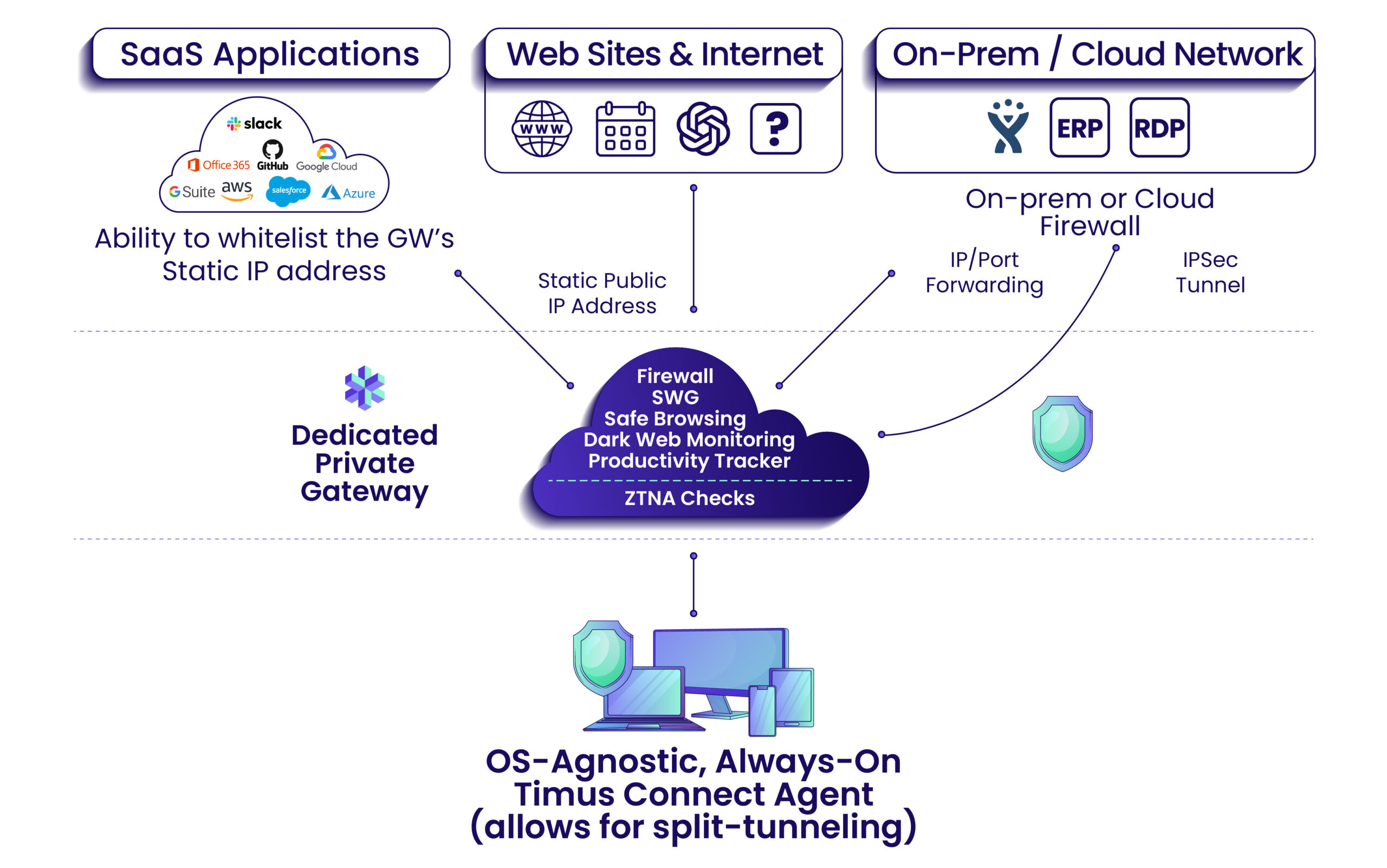
Timus provides a Software Defined Perimeter with the following key building blocks:
- Zero Trust Network Access with a rich set of behavior-based policies
- Always-on, OS-agnostic agent (Timus Connect App) to replace VPNs
- Adaptive Cloud Firewall that tracks users everywhere
- Dedicated Private Client Gateway with a Static IP
- Secure Web Gateway with web and category filtering
- Safe Browsing, and Dark Web Monitoring
- Productivity Tracker
- A multi-tenant Partner Portal for Managed Service Providers (MSPs) to onboard and manage clients from a centralized single pane of glass
The Key Benefits of ZTNA
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) offers a wide range of benefits that make it an attractive security solution for modern organizations. As businesses continue to shift towards remote and hybrid work, cloud-based applications, and distributed environments, ZTNA addresses critical security concerns by enforcing the principle of “never trust, always verify.” In this section we will dive deeper into the key benefits of ZTNA and how it enhances the security posture of an organization.
1. Reduced Attack Surface
ZTNA drastically reduces the attack surface by limiting access only to specific applications and resources that a user needs to perform their job. Unlike traditional VPNs, which grant access to the entire network once authenticated, ZTNA provides granular, application-level access. This ensures that even if an attacker gains unauthorized access through compromised credentials, they won’t be able to move laterally across the network and access other critical systems.
2. Improved User Experience
ZTNA enhances the user experience by enabling seamless access to applications, particularly for remote and hybrid workers. Traditional VPNs often introduce latency and performance bottlenecks because they route all traffic through a centralized gateway, which can slow down application performance. ZTNA provides direct, secure access to applications, improving performance and making it easier for users to access resources without sacrificing security.
Example:
A remote employee working from home uses a VPN to access company resources, and all of their internet traffic must go through the VPN server, creating slowdowns. With ZTNA, the employee directly connects to specific applications through secure encrypted IPSec tunnels, reducing latency and providing faster, more reliable access to the tools they need to complete their tasks.
Additionally, ZTNA solutions are cloud-native and integrate well with cloud applications, ensuring a smooth user experience regardless of the application’s location—whether on-premises or in the cloud.
3. Granular Access Control
ZTNA operates on the principle of least privilege access, ensuring that users only have access to the applications and data they need, and nothing more. This granular access control limits the potential for misuse or unauthorized access, even if a user’s credentials are compromised. The fine-tuned control over access levels helps to minimize the risk of insider threats, accidental data exposure, or unauthorized access to sensitive information.
ZTNA enforces access control based on a variety of factors such as user identity, device status, and contextual elements (e.g., location, time of access). By continuously verifying the legitimacy of access requests, ZTNA ensures that only authorized users and devices can interact with protected applications.
4. Enhanced Security for Remote Work
One of the key benefits of ZTNA is its ability to secure access for remote workers, which has become increasingly important in the age of hybrid work models. Traditional security models, like VPNs, are designed for users within a company’s physical premises, making them less suitable for employees working from various locations, including homes, cafes, or co-working spaces.
ZTNA addresses this by securing access regardless of location or device, ensuring that remote employees can connect securely to the applications they need, without the risks associated with traditional perimeter-based security models.
Let’s look at an example that most of us lived through: During the COVID-19 pandemic, many organizations shifted to remote work. Employees were logging in from various locations and often using personal devices, increasing the risk of cyber threats. ZTNA provided these organizations with a flexible and scalable solution that secured access to corporate resources without the need for a traditional network perimeter, ensuring employees could work safely from anywhere.
ZTNA also supports the concept of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) by ensuring that non-corporate devices, such as employees’ personal smartphones or laptops, can only access corporate applications after passing strict security checks.
5. Improved Scalability and Flexibility
ZTNA is a cloud-native solution that is inherently scalable and flexible, making it easier for organizations to grow or shrink their operations without the need for extensive infrastructure upgrades. Whether an organization is adding new employees, shifting to a remote workforce, or adopting new cloud-based applications, ZTNA can seamlessly accommodate these changes.
Traditional security models often require significant investments in hardware (like VPN concentrators) to scale up, which can be costly and complex. With ZTNA, scaling is more straightforward, as security is delivered through the cloud and managed centrally.
For example, an organization rapidly hires remote workers and needs to provide them with secure access to applications hosted in the cloud. Instead of setting up additional VPN infrastructure, the organization can use ZTNA to quickly and securely onboard new users and provide access to specific applications, no matter where the users are located.
This flexibility also applies to multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environments. ZTNA ensures that users can securely access resources across different environments without the complexity of configuring multiple security solutions.
6. Contextual and Continuous Authentication
Unlike traditional access controls that authenticate users once at login, ZTNA relies on continuous authentication. It evaluates contextual factors such as the user’s behavior, device status, location, and time of day to assess whether access should be granted or maintained. If a user’s behavior or device status changes during a session, ZTNA can revoke or limit access in real time, ensuring that users remain trustworthy throughout their session.
7. Seamless Integration with Cloud Services
As more organizations migrate their workloads to cloud environments, securing access to cloud-based applications has become a top priority. ZTNA is designed to work seamlessly with cloud services such as SaaS (Software as a Service) applications and multi-cloud architectures. It provides secure, direct access to cloud applications without requiring users to route their traffic through a corporate network or VPN.
ZTNA’s integration with cloud services simplifies security management and enhances the user experience by allowing users to connect directly to the applications they need in the cloud.
Example: An organization using a mix of cloud services, such as Microsoft Office 365 and AWS-hosted applications, can leverage ZTNA to provide secure access to these services. Remote workers can connect directly to the cloud applications they need, without routing their traffic through the company’s network, reducing latency and improving performance.
8. Cost-Effectiveness
While traditional security models, such as VPNs and on-premise security infrastructure, often require significant investments in hardware, maintenance, and operational management, ZTNA is typically more cost-effective. ZTNA is cloud-native and does not require expensive hardware appliances, making it easier to implement and maintain.
In addition, ZTNA’s scalability means that organizations can easily adjust the number of users or applications they need to secure without purchasing additional hardware or reconfiguring complex systems.
What is SASE and How Does it Integrate with ZTNA?
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) is a cloud-native architecture that combines wide-area networking (WAN) capabilities with comprehensive security services. It unifies various security functions—including ZTNA, Secure Web Gateway (SWG), Firewall as a Service (FWaaS), and Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)—into a single platform.
SASE delivers these services through the cloud, allowing organizations to securely connect users to applications and data across distributed environments, whether they are on-premises, in the cloud, or remote. The primary goal of SASE is to simplify the management of both networking and security functions while enhancing security posture through a Zero Trust approach.
How ZTNA Fits into SASE?
Within the SASE framework, ZTNA is the mechanism that enforces access control. While SASE provides the overall infrastructure to secure and manage access to resources, ZTNA ensures that access is granted only after the user’s identity, device health, and context have been verified.
This relationship is vital for modern organizations looking to secure access to their applications and data in a cloud-centric world. ZTNA provides the access control layer, while SASE ensures that all traffic, both internal and external, is securely routed and inspected for threats.
How Timus Networks Enables ZTNA within the SASE Framework
As a leading cybersecurity provider, Timus Networks integrates ZTNA into its comprehensive SASE solution, offering a unified platform that secures access to applications, data, and networks. Here’s how Timus Networks enables organizations to embrace ZTNA as part of a SASE strategy:
1. Cloud-Native ZTNA for Seamless Access
Timus Networks provides a cloud-native ZTNA that integrates with the broader SASE solution architecture. This ensures that users—whether they are remote, mobile, or on-premises—can securely access only the applications they need without being exposed to the entire network. By continuously verifying user identities and device compliance, Timus’ ZTNA ensures that access is tightly controlled, reducing the risk of unauthorized entry.
2. Granular, Least-Privilege Access Control
Timus Networks empowers organizations to apply least-privilege access principles, granting users only the minimum level of access required for their tasks. This granular control helps reduce the risk of overexposure, as users can access only the applications or data they are authorized to use. Timus ZTNA dynamically adjusts access based on user identity, device health, and contextual factors such as time and location.
3. Simplified, Centralized Security Management
With Timus Networks’ integrated SASE platform, organizations can manage all security and networking functions from a single console. This centralization simplifies operations, reduces complexity, and ensures consistent policy enforcement across cloud and on-premises environments.
4. Scalability for Distributed Workforces
Timus Networks’ SASE and ZTNA solutions are built to scale, supporting organizations with dynamic security needs. Whether an organization is expanding its remote workforce or migrating more applications to the cloud, Timus’ cloud-native architecture scales effortlessly. This flexibility ensures that security is maintained as business needs evolve, without requiring significant infrastructure investments.
5. Optimized Remote Access
Traditional VPNs often introduce performance bottlenecks and security risks, especially for remote workers. Timus Networks addresses this challenge by providing always-on, secure remote access through ZTNA. This approach allows remote users to securely access cloud and on-premises applications directly without the need for traffic to be routed through a centralized VPN gateway. The result is faster, more reliable connections and improved productivity for remote employees.
6. End-to-End Security with Real-Time Threat Detection
Timus Networks’ SASE platform incorporates real-time threat detection, encryption, and continuous monitoring, ensuring that all traffic is inspected for malicious activity. By integrating ZTNA into this architecture, Timus ensures that secure connections are established between users and applications, while also protecting against external and internal threats.
Why Timus Networks is a Leader in ZTNA and SASE?
As organizations continue to adopt cloud-based solutions and remote work models, the need for a unified, secure access solution has never been more urgent. Timus Networks stands out as a leading security provider in both ZTNA and SASE by providing innovative, cloud-native solutions that enable secure, scalable access to applications and data. With its focus on Zero Trust principles, Timus helps organizations protect their digital infrastructure while improving user experience and reducing complexity.
Conclusion: Embracing a Zero Trust Future
In the age of distributed workforces and cloud-first strategies, traditional security models are no longer enough. By integrating ZTNA into its SASE platform, Timus Networks enables organizations to adopt a Zero Trust approach that enhances security, reduces risk, and delivers a seamless user experience. Whether securing remote access, managing hybrid environments, or scaling for growth, Timus Networks provides the tools needed to navigate the challenges of modern cybersecurity.
As businesses continue to evolve, embracing a Zero Trust Network Access model through a robust SASE framework will be key to staying ahead of security threats while empowering users to securely access the applications they need. With Timus Networks, organizations can confidently embrace the future of secure access.
By focusing on both ZTNA and SASE, Timus Networks ensures that your organization is not only protected today but prepared for the security challenges of tomorrow.
FAQs
Yes, Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) can replace traditional VPNs in many cases. Unlike VPNs, which provide broad access to an entire network, ZTNA grants access only to specific applications or resources based on the user’s identity, device health, and context. This reduces the attack surface and minimizes the risk of lateral movement if credentials are compromised. Additionally, ZTNA provides better scalability, performance, and security in cloud-centric environments compared to VPNs, making it an ideal replacement for organizations moving toward a Zero Trust security model.
A firewall is a network security device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined security rules. It typically operates at the network level, forming a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks (like the internet). Firewalls are perimeter-based and often focus on allowing or blocking traffic based on IP addresses, ports, or protocols.
ZTNA, on the other hand, is a more advanced security model that operates on the principle of Zero Trust, requiring continuous identity verification before granting access to specific applications or resources. ZTNA does not rely on predefined network perimeters; instead, it works on an identity-based access model and ensures that access is granted only after verifying multiple factors such as user identity, device health, and contextual data. While firewalls are effective at securing the network perimeter, ZTNA focuses on securing access to applications and data, regardless of the network location.
While Zero Trust can incorporate password-less authentication mechanisms, such as biometrics, tokens, or multi-factor authentication (MFA), it is not inherently password-less. The key concept in Zero Trust is the requirement for continuous verification, which may or may not include passwords. Password-less authentication methods are becoming more common in Zero Trust architectures as organizations aim to reduce the risks associated with stolen or weak passwords, but the focus remains on using multiple forms of identity verification rather than relying solely on one method like passwords.
Yes, Zero Trust is closely aligned with the principle of least privilege access. This principle dictates that users and devices should have access only to the resources they need to perform their tasks, and no more. Zero Trust enforces least privilege access by continuously verifying user identity, device health, and contextual factors before granting access to specific applications or data. By ensuring that access is limited and conditional, Zero Trust minimizes the risk of overexposure or lateral movement within the network in the event of a breach.
Zero Trust is beneficial for organizations of all sizes, across all industries, but it is especially important for those that rely on distributed workforces, cloud-based applications, and hybrid environments. Key examples include:
– Organizations with remote or hybrid workforces: Zero Trust ensures secure access to applications and data from any location, on any device.
– Enterprises using cloud services: As cloud adoption increases, organizations need a way to securely connect users to cloud-based applications without exposing the network.
– Highly regulated industries: Industries like healthcare, finance, and government often require strict access controls and compliance with data protection regulations (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR). Zero Trust helps ensure that access to sensitive data is tightly controlled and continuously monitored.
– Companies experiencing digital transformation: As companies migrate their infrastructure to the cloud and adopt new technologies, Zero Trust helps protect their evolving IT environments by minimizing security risks.
In essence, any organization looking to enhance its cybersecurity posture, particularly in the face of growing threats like ransomware, insider threats, or cloud-based attacks, would benefit from implementing Zero Trust.